When you're starting out, the world of microphones can seem overwhelming. You'll hear terms like dynamic, condenser, and ribbon thrown around, but what do they actually mean? At their core, these are just different ways of capturing sound. Each type uses a unique internal design, which gives it a distinct personality and makes it perfect for some jobs but not so great for others.
Your Guide to Choosing the Right Microphone

Honestly, picking the right microphone is probably the single biggest decision you'll make in your quest for pro-level sound. It’s the very first link in your recording chain. Get it wrong, and you'll be fighting an uphill battle from the start.
But don't let that intimidate you. Think of it like this: you wouldn't use a sledgehammer to hang a picture frame, right? The same logic applies here. This guide is designed to cut through the confusing tech-speak and give you a practical understanding of how these tools work. We'll look at why a tough-as-nails dynamic mic is the go-to for a roaring guitar amp, and why a super-sensitive condenser is the secret to those crystal-clear studio vocals.
Matching the Mic to the Moment
Before you even think about buying a mic, ask yourself one simple question: "What am I trying to record?" The answer changes everything. Are you capturing the thunderous attack of a drum kit, the delicate fingerpicking on an acoustic guitar, or the nuanced conversation of a podcast? Each of these sound sources has a perfect microphone match.
A dynamic mic, for instance, is the workhorse of the stage and studio because it can take a beating and handle incredibly loud sounds without flinching. A condenser, on the other hand, is all about capturing the finest details with stunning clarity. And then you have ribbon mics, which are prized for their vintage warmth and uncanny ability to smooth out harsh, brittle frequencies.
Getting a feel for these core personalities is the first real step toward making a choice you'll be happy with. Even if you're working with a tight budget, knowing the fundamentals will help you find a fantastic microphone. We've actually put together a list of the best budget microphones for recording vocals that proves you don't need to spend a fortune.
This growing demand for high-quality audio tools is making a real impact. The global microphone market was valued at an impressive USD 2.45 billion in 2023 and is expected to climb to USD 3.53 billion by 2028. It’s all driven by new technology and more people than ever creating their own content. You can learn more about these microphone market trends and what's behind the growth.
Key Takeaway: There is no single "best" microphone. The right microphone is always the one that best complements your sound source, your recording space, and the creative vision you're trying to achieve.
To give you a head start, I've put together a simple table that cuts right to the chase. It’s a quick-glance guide to help you match common recording tasks with the microphone type best suited for the job.
Quick Guide to Microphone Types and Common Uses
| Microphone Type | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic | Loud sources like guitar amps, drums, live vocals | Durability and handling high sound pressure |
| Condenser | Studio vocals, acoustic instruments, overheads | Sensitivity and capturing fine detail |
| Ribbon | Taming harsh sounds, electric guitar, brass | Natural, warm, and smooth sound |
Think of this as your cheat sheet. When in doubt, refer back to it, and you'll be on the right track to capturing the sound you hear in your head.
Dynamic Mics: The Workhorses of Recording

If the audio world has a trusty, reliable tool that shows up to work every single day, it's the dynamic microphone. These mics are legendary for their simple, powerful design and sheer toughness. They are the undisputed champions for capturing loud, aggressive sounds without breaking a sweat—or, more importantly, distorting your recording.
Think of a dynamic mic as a tiny speaker working in reverse. Inside, a diaphragm is attached to a coil of wire that sits inside a magnetic field. When sound waves hit that diaphragm, it moves the coil back and forth, generating a small electrical signal that directly mirrors the original sound. It's this beautifully simple, magnet-and-coil engine that makes them so incredibly durable.
Built for Power and Durability
The core strength of a dynamic microphone is its ability to handle extremely high sound pressure levels (SPL). This makes them the go-to choice for sound sources that would completely overwhelm more sensitive microphones.
- Guitar Amplifiers: You can shove them right up against a speaker cone that's blasting at full volume to capture raw, punchy tone without any unwanted breakup.
- Snare Drums & Toms: Their knack for handling sharp, percussive hits is why you'll find them on nearly every drum kit in a recording studio.
- Rock & Metal Vocals: For powerful singers who really belt it out, a dynamic mic captures all that energy without clipping or distorting.
A huge advantage here is their independence. Dynamic mics are passive, which means they do not require any external power (like phantom power) to operate. You just plug them in and they work—simple as that. This makes them perfect for both demanding live sound and straightforward studio setups.
This resilience and plug-and-play nature have made them incredibly popular, especially in handheld form. The global market reflects this, with handheld microphones being the dominant segment—projected to grow from USD 1.23 billion in 2022 to USD 1.76 billion by 2032. It’s clear there's a sustained demand for mics that can be used everywhere from the stage to the studio. You can discover more insights about these microphone statistics and see their market impact for yourself.
Trade-Offs and Ideal Applications
Of course, no single microphone is perfect for every task. The rugged build of a dynamic mic means it's generally less sensitive to very subtle, high-frequency details when compared to its condenser cousins. It might not capture the airy sparkle of a delicate acoustic guitar or the breathy texture of a soft vocal performance with the same pristine clarity.
But this "limitation" is often a strength in disguise. Their lower sensitivity helps them naturally reject background noise and room reflections, making them a fantastic choice for recording in less-than-perfect acoustic spaces. This focused pickup is exactly why they're a favorite for home studio podcasters and streamers.
When you're ready to make a decision, our guide on how to choose the best music production microphone can help you weigh these pros and cons for your specific needs.
Condenser Mics: Capturing Every Last Detail

If dynamic mics are the trusty workhorses of the stage, condenser microphones are the high-performance instruments of the studio. They're famous for their incredible sensitivity and knack for capturing sound with stunning, lifelike detail. When you need to hear the subtle breath in a singer's voice or the shimmering tail of a cymbal crash, you reach for a condenser.
So, how do they do it? The secret is in a design that works like a capacitor. Imagine two metal plates with a voltage running between them. In a condenser mic, one of these plates is a fixed backplate, while the other is an incredibly thin, lightweight diaphragm that moves when sound waves hit it.
As the diaphragm vibrates, the distance between it and the backplate changes. This fluctuation alters the capacitance and creates an electrical signal that’s a near-perfect mirror of the original sound. It’s a very delicate and precise mechanism, but it needs power to work. That’s where +48V phantom power comes in—a standard feature on most audio interfaces that sends a small electrical charge down the mic cable.
Large vs. Small Diaphragm Condensers
Condensers aren't a one-size-fits-all tool. They mainly come in two flavors, and knowing the difference will make or break your recording.
1. Large-Diaphragm Condensers (LDCs)
These are the mics you probably picture when you think of a recording studio. With a diaphragm of an inch or more, LDCs are prized for the warmth and richness they bring to a recording. They tend to add a flattering, larger-than-life character, which is exactly why they are the go-to choice for lead vocals in most professional studios.
2. Small-Diaphragm Condensers (SDCs)
Often called "pencil mics" for their slender, cylindrical shape, SDCs are the masters of accuracy. They have a lightning-fast transient response, meaning they can capture sharp, percussive sounds with incredible precision. This makes them perfect for recording the crisp attack of an acoustic guitar, the complex wash of drum overheads, or the articulate "chick" of a hi-hat.
The real choice between an LDC and an SDC comes down to character versus accuracy. An LDC often adds a beautiful sonic color that enhances the source, while an SDC strives to capture it with unflinching, transparent honesty.
The Good and the Bad of Condenser Mics
Deciding whether a condenser is right for your needs means balancing its incredible strengths against its particular demands.
- Pro: Superior Detail and Clarity – They pick up a huge range of frequencies and all the subtle textures other mics can miss, giving you that crisp, polished sound.
- Pro: Excellent Transient Response – Perfect for capturing intricate, percussive sounds with jaw-dropping realism.
- Con: Require Phantom Power – No exceptions here. You need an audio interface or mixer that can supply that +48V charge.
- Con: A Bit Fragile – Their sensitive internal parts mean they can't take a beating like a dynamic mic can. A drop or exposure to extremely loud sounds can cause real damage.
- Con: They Hear Everything – This is a double-edged sword. Their sensitivity will capture every beautiful nuance, but it will also pick up every car driving by, every air conditioner hum, and every echo in an untreated room.
The Timeless Warmth of Ribbon Microphones
If dynamic and condenser mics are the workhorses of the studio, then ribbon mics are the prized thoroughbreds. Opening a ribbon mic case feels like uncovering a piece of history, and for good reason. These microphones are behind the silky-smooth, incredibly natural sound of so many legendary recordings, especially from the golden age of broadcasting and music.
Their magic lies in a design that is both elegant and deceptively simple. Inside, a super-thin, corrugated ribbon of aluminum is suspended in a powerful magnetic field. That's it. As sound waves hit this delicate ribbon, it vibrates, creating a tiny electrical current. This mechanism is what gives ribbon mics their signature sound—a sound many engineers feel is the closest you can get to what our ears actually hear in a room.
The result is a frequency response that is famously smooth. Ribbon mics have an uncanny ability to tame harshness in the upper frequencies, rolling them off in a way that sounds musical, not muffled. This isn't a bug; it's their most sought-after feature.
A Secret Weapon for Taming Harshness
That gentle high-end roll-off is precisely why an experienced engineer reaches for a ribbon. It’s the perfect tool for capturing sources that might otherwise sound brittle, shrill, or overly aggressive.
This is where they truly excel:
- Electric Guitar Amps: A ribbon mic in front of a roaring guitar amp is a classic pairing. It shaves off the unpleasant, fizzy distortion, leaving you with a thick, weighty tone that cuts through a mix without hurting your ears.
- Brass Instruments: Trumpets and trombones can easily sound piercing. A ribbon captures their full power and body while softening any metallic "ice-pick" frequencies, resulting in a warm, commanding sound.
- Drum Overheads: When used as overheads, ribbons offer a beautifully dark and cohesive snapshot of the entire kit. Cymbals sound less like crashes and more like musical shimmers.
Getting Creative with the Figure-8 Pattern
Almost all traditional ribbon mics have a native bidirectional polar pattern, also known as figure-8. This means they pick up sound equally from the front and the back, while almost completely ignoring sound from the sides. Far from being a limitation, this opens up a world of creative recording possibilities.
For instance, you could place one ribbon mic between two harmony singers, capturing both performers with a single microphone. Or, try recording a singer-songwriter by aiming the front of the mic at their acoustic guitar and the rear lobe up toward their mouth. You get great separation and a cohesive sound.
The rear side of the mic doesn't just capture another source; it also captures the sound of your room. This can add a beautiful, natural ambience to your recordings, giving them a sense of space and life that's hard to replicate with artificial reverb.
Of course, this classic design isn't without its quirks. Vintage ribbon mics are famously fragile; a blast of phantom power or even a strong plosive ("p" or "b" sound) could stretch or snap the delicate ribbon. They also produce a very low output signal, so you'll need a good preamplifier with plenty of clean, quiet gain to bring them up to a usable level.
Thankfully, modern advancements have tackled these old problems head-on. Many contemporary ribbon mics are built to be far more durable. Some are even active, with built-in electronics that boost the signal and make them phantom-power-safe. This marriage of vintage character and modern engineering makes today’s ribbon mics an incredible tool for anyone looking to add a touch of timeless warmth to their recordings.
Understanding Where Your Microphone Listens
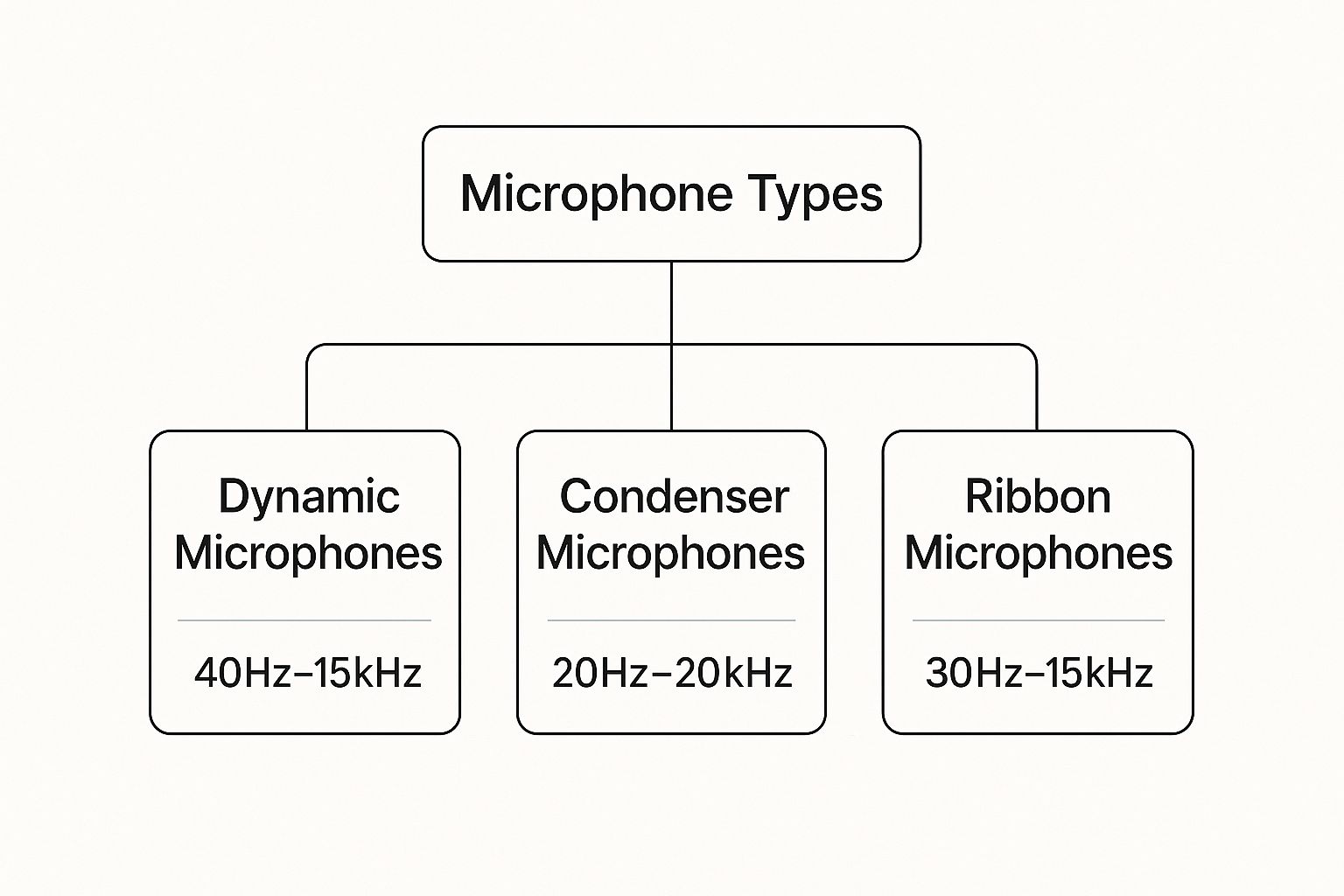
This infographic gives you a great visual on the typical frequency response for different mics. You can see how condenser mics often have that wider range, which is why they're known for capturing so much detail.
But knowing your microphone types for recording is only half the battle. The other, equally crucial piece of the puzzle is the microphone’s polar pattern. It’s a fancy term for a simple concept: a mic's directionality. It determines where the microphone "hears" sound from, and just as important, what sounds it ignores.
I like to think of a polar pattern like the beam of a flashlight. Some flashlights throw a huge, dim circle of light, catching a bit of everything in the room. Others shoot out a tight, powerful beam, lighting up one specific spot while everything else stays dark. Microphones do the exact same thing with sound.
Picking the right pattern is absolutely essential for getting a clean, professional recording. It’s your number one tool for separating what you want to hear from all the stuff you don't—like room echo, computer fans, or other musicians. Get this right, and your audio quality will take a giant leap forward.
The Most Common Pickup Patterns
Most of the time, you'll be working with one of three main polar patterns. Each one has a distinct shape and a job it excels at. If you can understand what makes them tick, you'll know exactly which mic to grab for any situation.
-
Cardioid: This is the workhorse of the recording world. It gets its name from its heart-shaped pickup area, capturing sound mostly from the front while rejecting noise from the sides and, especially, the back. This focused "beam" is your go-to for recording vocals or a single instrument because it helps shut out unwanted room noise.
-
Omnidirectional: Think of this as the "wide beam" flashlight. An omni mic hears everything equally from all directions—360 degrees. It's fantastic when you want to capture the total sound of a space, like the natural reverb of a beautiful hall or a group of people talking around a single microphone on a table.
-
Bidirectional (Figure-8): This one is a bit more specialized. It picks up sound perfectly from the front and the back, but it's almost completely deaf on the sides. This makes it the perfect tool for a two-person interview or podcast, where you can place the mic between two people facing each other.
Want to know why podcasters sound so close and personal? They're usually using a cardioid mic right in front of their mouth, which focuses only on their voice. Compare that to a typical lapel mic—often omnidirectional and clipped to a shirt—which picks up more of the room's sound, making the speaker feel farther away.
Tighter Patterns for Maximum Rejection
Sometimes, even a standard cardioid isn't focused enough. That's where you'll find specialized variations designed for extreme isolation. Supercardioid and Hypercardioid patterns take the cardioid concept and make the front-facing pickup angle even narrower.
This super-tight focus is a lifesaver on a loud stage where you need to prevent feedback, or in the studio when you want to isolate one part of a drum kit, like a hi-hat, from the snare right next to it.
But there’s a catch. This tighter front focus comes at a cost: these patterns introduce a small area of sensitivity directly behind the microphone. It’s a little blind spot you have to be aware of. If you’re not careful with placement, you might accidentally pick up a sound you were trying to avoid from behind the mic.
To make it easier to choose, here's a quick cheat sheet that breaks down what each pattern does best.
Polar Pattern At-a-Glance Comparison
| Polar Pattern | Pickup Angle | Best For | Rejects Sound From |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardioid | ~130 degrees (Front) | Vocals, solo instruments, podcasting, live performance | The rear and sides |
| Omnidirectional | 360 degrees | Room ambiance, group discussions, conference calls | Nowhere; it captures all directions |
| Bidirectional | Front and Rear | Two-person interviews, stereo recording (Blumlein) | The sides (90-degree angle) |
| Supercardioid | ~115 degrees (Very narrow front) | Isolating instruments on a loud stage, film dialogue | Most of the sides and rear, but has a small rear lobe |
| Hypercardioid | ~105 degrees (Extremely narrow front) | Maximum sound isolation, rejecting crosstalk | The sides, but has a larger rear lobe than supercardioid |
Think of this table not as a set of rigid rules, but as a starting point. The real magic happens when you start experimenting with these patterns in your own space and hear the difference for yourself.
How to Choose Your First Recording Microphone
Now that you've got a handle on the different microphone types and their polar patterns, it’s time for the fun part: picking your first mic. This decision isn't just about reading specs on a box. It's about finding the right tool for your voice, your room, and your budget.
Let's put this into a real-world context. Imagine you're a podcaster recording in a spare bedroom that hasn't been acoustically treated. A dynamic microphone is probably your best bet. Its focused pickup pattern and lower sensitivity will naturally ignore a lot of that distracting room echo and background hum.
On the other hand, if you’re a singer-songwriter aiming to capture every subtle nuance of your voice and acoustic guitar, a large-diaphragm condenser is a fantastic starting point. It's designed to pick up that rich detail and character.
Matching Your Mic to Your Budget
Your budget is obviously a huge part of the equation, but don't worry—great sound is achievable at almost any price point. Here’s a general idea of what you can expect to find.
- Entry-Level ($50 – $150): This is the sweet spot for fantastic USB mics and very capable entry-level XLR dynamic and condenser models. If you're just starting a podcast, streaming, or dipping your toes into home recording, this is where you should look.
- Intermediate ($150 – $400): Stepping up to this range gets you into industry-standard dynamic mics and some seriously good large-diaphragm condensers. You'll notice a real jump in clarity, build quality, and overall performance, making these perfect for musicians and creators who are getting serious.
- Professional ($400+): Welcome to the top tier. This is where you'll find premium condenser microphones, modern ribbon mics, and other specialized tools. These mics deliver exceptional detail and are built for the demands of a professional studio.
Remember, your microphone is just the first piece of the puzzle. You'll also need a few essentials to get clean, professional results: a pop filter to tame those harsh "p" and "b" sounds, a solid mic stand that won't wobble, and, if you go with an XLR mic, a quality audio interface to connect it all to your computer.
It's also worth noting how the market is evolving. Digital microphones held the largest market share in 2022, largely because they offer a great signal-to-noise ratio and plug-and-play simplicity with modern devices. This trend, combined with the rise of wireless technology, points toward a future of flexible, high-quality recording becoming even more accessible. If you're curious about the tech trends, you can read more about these microphone market drivers and see where things are headed.
Ultimately, picking your first microphone is a foundational step on an incredibly rewarding journey. For a more detailed look at setting up for singing, be sure to check out our complete guide on how to record vocals at home. A smart choice now will pay off for years to come, setting you up to create audio you can truly be proud of.
A Few Common Questions We Hear All the Time
Diving into the world of microphones always brings up a few practical questions. Let's tackle some of the ones that come up most often for creators just getting started.
What's the Best "Do-It-All" Mic for a Home Studio?
If you’re looking for one microphone to cover as much ground as possible, a large-diaphragm condenser is almost always the right answer. These mics are champs at capturing the nuance and detail in vocals and acoustic instruments, giving you that crisp, professional sound right from the start.
To really get the most out of it, try to find one with switchable polar patterns. Being able to flip between cardioid for a focused vocal and omni for a roomy acoustic guitar makes a single mic feel like two or three.
Does My Mic Need Phantom Power?
You'll only need to flip that +48V phantom power switch if you're using a condenser microphone. It's a tiny electrical current that their internal electronics need to work.
Dynamic mics and most ribbon mics, on the other hand, don't need any external power at all. Just plug them in and you're good to go. Thankfully, pretty much every modern audio interface has a simple button to turn phantom power on when you need it.
Key Insight: A USB microphone is an all-in-one solution with a built-in preamp that plugs directly into your computer. An XLR microphone is the professional standard, requiring an external audio interface and cable. While USB is simpler, an XLR setup offers higher quality and the ability to upgrade individual components over time.
Is a Pop Filter Really That Important for Vocals?
Yes, absolutely. A pop filter is a non-negotiable, must-have piece of gear for recording vocals. It's a simple mesh screen that sits between the singer and the mic, but its job is critical: it stops plosives.
What are plosives? They're those distracting bursts of air from "p" and "b" sounds that hit the microphone's diaphragm and create a boomy, unpleasant thump in your recording. It’s a cheap tool that saves you a massive headache in the mixing stage and instantly makes your recordings sound more professional.
Ready to turn your musical ideas into polished tracks? At ChordX, we provide the expert guides, in-depth tutorials, and unbiased reviews you need to elevate your sound. Discover how to build your ideal studio and refine your production skills at chordx.io.



